How does a player come to love a game? By analyzing the behavior of millions of Candy Crush Saga players scientists quantified progression and churn as a competition between relative difficulty and engagement.
- From 2014 to 2016 scientists studied a cohort of almost 12 million Candy Crush Saga players.
- Scientists used the accumulated number of attempts to measure activity, and the maximum level achieved after a given number of attempts to measure progress.
- There were two competing processes:
- The number of attempts required for any given player to pass a level.
- The number of attempts it takes any given player to become bored and abandon the game.
- Level of engagement in casual games shows a scaling behavior (happy-get-happier, as the scientists put it) described by a power-law that is a function of a player’s progression.
- Difficult/traumatic experiences in initial game stages lead to massive churn.
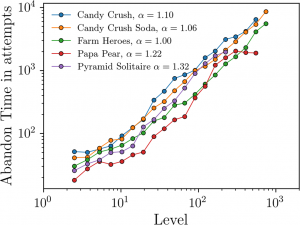
- This analysis was repeated with Farm Heroes, Papa Pear, Candy Crush Soda, and Pyramid Solitaire.
- All of these games exhibited the same power-law behavior of engagement.
- Data analyzed from different continents, platforms, and periods of time showed the same behavior.
- Evolution of engagement may be universal.
Full Nature article
Reguera, D., Colomer-de-Simón, P., Encinas, I. et al. Quantifying Human Engagement into Playful Activities. Sci Rep 10, 4145 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-60742-8
